Regulatory Compliance Management Software for Healthcare
In healthcare software development since 2005, ScienceSoft engineers program-grade compliance platforms for the sector, covering policies, training, controls, risk management, audit readiness, and response. Our Medical Doctor (MD) compliance consultants help healthcare organizations adhere to HIPAA, HITECH, CMS Conditions of Participation, OSHA, and state-level mandates.
Healthcare regulatory compliance software is meant to act as a centralized, highly integrated hub for policy management, document tracking, staff training, risk monitoring, and reporting, reducing the risk of errors and non-compliance across the organization.
Custom compliance systems that are tightly connected to other enterprise software and third-party data sources can ingest and structure compliance evidence in a machine-readable format across the whole IT ecosystem, keep a live vendor inventory mapped to PHI categories, risk tiers, and control documentations, and automate workforce and vendor screening with the scope and cadence regulators expect.
- Valuable integrations for compliance software: EHR, HRIS, ERP/vendor portals, LMS, credentialing/privileging software, ticketing software.
- Implementation time: 6 to 12+ months.
- Development costs: $80,000–$600,000+.
Core Capabilities of Regulatory Compliance Management Software in Healthcare
Policy and document management
Training and education management
Risk assessment and management
Incident reporting and management
Vendor and third-party management
Audit and inspection readiness
Workflow automation
How Secure AI Tools Can Streamline Compliance Management
Automated policy gap detection
Specialized AI models scan uploaded policy documents and map them to current federal and state requirements (e.g., HIPAA, OSHA, CMS). The system flags missing or outdated sections, cites the specific clause, and shows “last updated” dates so teams can verify what changed and why. For each flagged gap, reviewers see side-by-side excerpts with suggested language pulled from internal templates. A mandatory human review step ensures that updates are approved by compliance or legal before publication, and every decision is logged for auditability.
Smart document summarization and recommendations
Natural Language Processing (NLP) models can summarize lengthy compliance documents into role-based briefs with plain-English action items for staff. Each summary includes inline source citations and confidence notes, so reviewers know what to verify. Approval workflows route summaries to legal and clinical leadership before distribution; the system records who approved, when, and what changed.
Personalized learning paths
AI can analyze employee roles, prior training performance, and historical compliance gaps to automatically assign tailored training modules. An intelligent engine can recommend refresher micro-modules when quiz results show weak areas. Learning recommendations are always surfaced to managers for approval and are periodically reviewed for fairness and job relevance.
Proactive risk scoring
Machine learning models can analyze historical incident reports, audit findings, and policy acknowledgments to highlight where breaches or compliance failures are most likely. Dashboards show risk “hot spots” by department, site, or process, along with top contributing factors (e.g., late training, repeated documentation errors). Scores are accompanied by plain-language rationales and confidence ranges, and any intervention that affects staff workflows requires a human decision and is documented with the evidence considered.
Anomaly detection in incident reporting
AI can detect unusual patterns in incident submissions (e.g., sudden spikes in privacy complaints or underreporting in certain units) and alert compliance managers for further investigation. Each alert includes an explainable feature breakdown (what drove the signal), example cases, and suggested next steps (e.g., targeted refresher training). False-positive handling and feedback loops allow investigators to mark alerts as resolved or dismissed, improving future detection accuracy.
Continuous regulatory intelligence
Crawler engines can monitor updates from federal and state sources (e.g., HHS, CMS, state health departments) and triage what’s relevant to your organization’s footprint. AI classifies each change (policy, notice, enforcement, guidance), maps it to affected policies or training, and proposes updates with citations and change logs. Compliance or legal teams retain final control: changes only publish after their review. All data sources are recorded for provenance, and administrators can pause or defer updates for contested rules.
AI-driven task routing
For incidents, policy updates, or corrective actions, AI evaluates type, severity, specialty, and current workload to propose the best task owner and due date. Routing suggestions factor in credentials, shift patterns, and conflict-of-interest rules. Managers can approve or override assignments with one click, and the system records the rationale to improve future recommendations. Built-in guardrails support fairness reviews (periodic checks for disparate impact across groups), with an appeal path for staff.
Automated evidence gathering for audits
AI assembles policy acknowledgments, training records, incident timelines, and remediation artifacts into audit-ready packages aligned to the survey scope. Pre-filled report templates include source references and completeness checks (e.g., missing signatures, expired licenses). Compliance leads can add narrative context and lock the package for review. Chain-of-custody logs show when evidence was added or changed, by whom, and on what basis.
What Systems to Connect With Your Compliance Tracking Software
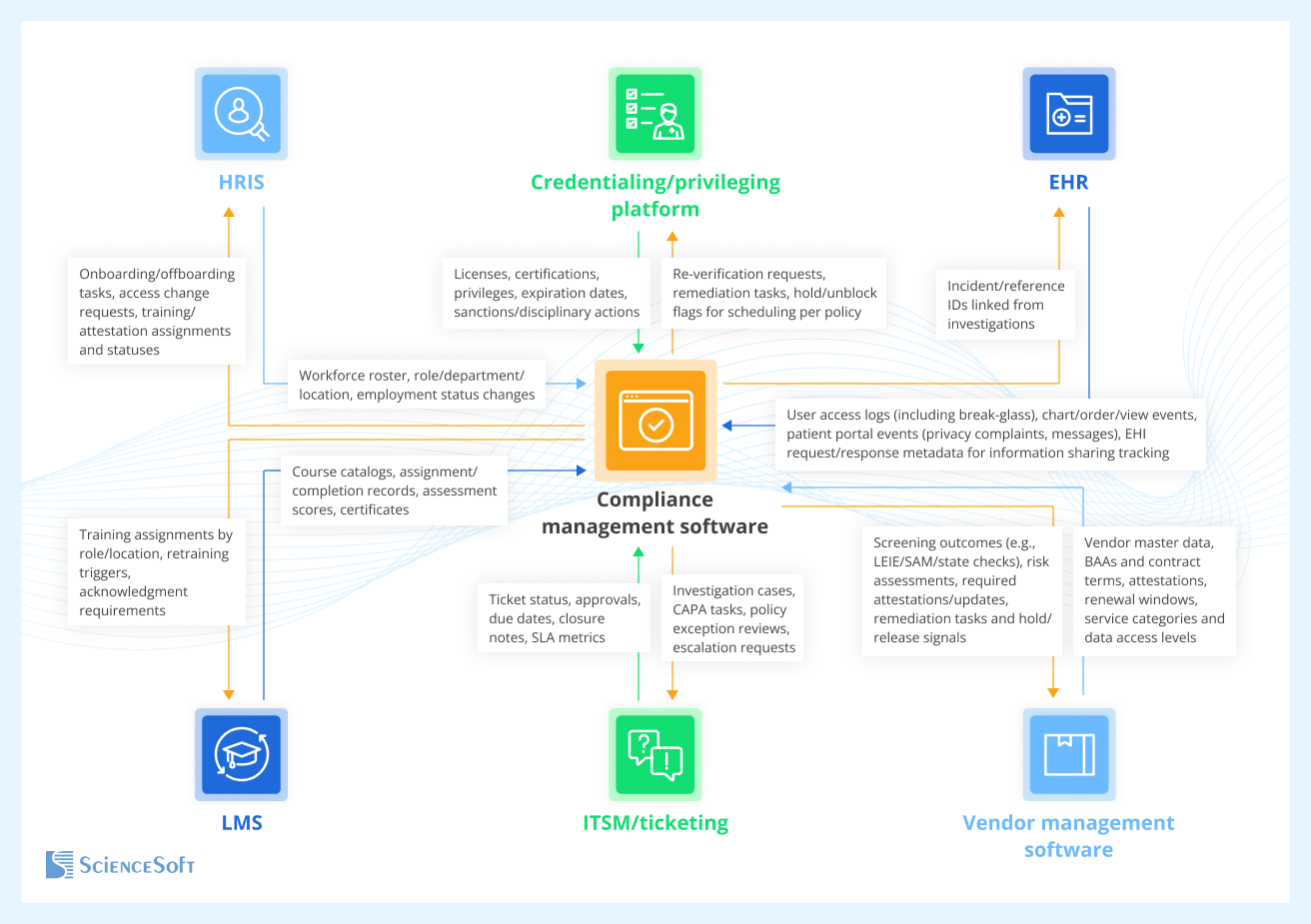
- HR systems to sync workforce rosters, roles, departments, and locations; trigger onboarding or offboarding tasks, training assignment, access changes, and audit-ready attestations.
- Credentialing or privileging software to pull licenses, certifications, privileges, and expiration dates; block scheduling or system access per policy; create remediation tasks.
- Electronic health records (EHR) to ingest access logs (including break-glass), chart or order touches, and patient-portal events (e.g., privacy complaints); tie incidents to patients or units and support information sharing exception documentation.
- Learning management system (LMS) to auto-assign training by role or location, track completions and assessments, store certificates, and feed reviewer dashboards and survey packets.
- IT service management (ITSM) / ticketing systems to route investigations and corrective actions (CAPA), record approvals and due dates, and measure SLA performance.
- ERP, vendor management platforms, or supply chain portals to maintain vendor inventories, BAAs, contracts, attestations, and renewal windows; trigger third-party risk reviews and evidence collection.
How to Build Software for Regulatory Compliance Management
Below, we provide a high-level overview of the key steps required to develop a comprehensive healthcare compliance management system. This plan is flexible and can be adapted to the specific regulatory environment, organizational structure, and existing IT infrastructure of any healthcare entity.
1.
Discovery and requirement gathering
Business analysts work together with compliance officers, legal counsel, risk managers, and department leaders (such as HR, IT, and Clinical Operations) to define which obligations the system must track and what evidence it needs to produce. They map current policies, regulatory requirements, and accreditation criteria into specific, measurable controls with defined data sources, owners, review schedules, and escalation paths. The team also specifies which systems will generate compliance events (for example, EHR, HRIS, LMS, or ticketing tools), what log formats and identifiers will be used, how often reviews will occur, what attestation methods are acceptable, and how evidence will be retrieved for audits or investigations. As a final step, the team ensures that the monitoring routines and audit workflows defined for the new software address the risks and compliance gaps identified during the organization’s latest compliance assessment.
2.
Architecture design
Architects review requirements and constraints and prioritize the quality attributes most critical for success, such as scalability, interoperability, or audit readiness. They select an appropriate architectural style, document trade-offs, and break the system down into modules with clear responsibilities. These modules and their interactions are represented in a system diagram showing components, data flows, and deployment layout. For each module, concise component specifications outline interfaces, data formats, and protocols; where an assumption is risky, a small proof of concept can be built to test critical aspects and address any identified risks.
Next, the team evaluates technologies for fit and maintenance, documents alternatives, and shapes an integration and API strategy that names connection points, payloads, sync triggers, and error handling.
In parallel, security engineers prepare a security architecture plan with identity management, access control, encryption, logging, data retention, and incident response procedures.
3.
UX/UI design
Designers begin with user research, recruiting representatives from target user groups to participate in interviews, task shadowing, and short surveys. This helps them understand how compliance reviews, audits, complaints, investigations, and board reporting are handled today. Findings become personas, task models, and an information architecture that names core objects (events, reviews, investigations, corrective actions, evidence) and the relationships between them. From there, designers outline task flows, test them with low-fidelity wireframes, and refine them through quick feedback loops with end users and compliance stakeholders. When a concept holds up, they switch to clickable prototypes to test navigation, data density, and error handling. Once the flows are validated, the interface is refined. Content designers write field labels, help text, and empty states in plain language, and compliance officers review the wording so statuses and warnings align with policy terminology.
Interaction design focuses on making compliance work easier to follow and less error-prone. For example, alerts can be designed to expand to show the specific rule text and the exact data that triggered it. This gives reviewers clarity and speeds resolution. Similarly, reviewers and auditors often struggle to track changes across reviews, so the interface can provide a “what changed since last review” mode that highlights updated policies, reassigned control or task owners, or shifts in risk metrics. Small UI additions can be made (e.g., a progress bar while evidence bundles compile or a clear “saved” signal when an incident note is logged) to reassure staff that their actions have been captured correctly.
4.
Development and testing
Developers build the system’s front end and back end, following unified coding practices and running regular code reviews. Delivery starts with core modules that address immediate compliance needs and reduce manual effort (e.g., policy and document management, training and certification tracking, risk assessment and monitoring, incident reporting, and vendor oversight). These foundations are prioritized because they directly support audit readiness, give leadership tangible dashboards, and automate the most resource-intensive compliance tasks. Once the basics are in place, more advanced capabilities can be layered on that rely on deeper integrations and complex automation (proactive risk scoring, AI-assisted anomaly detection, etc.).
In parallel, the QA and testing team simulates unauthorized access, policy violations, and process gaps to confirm event capture, reviewer workflow, exception handling, and corrective action tracking. They verify that scheduled monitoring runs when planned, tasks reach the right roles, attestations are recorded, and evidence bundles are consistent.
Learn more about how we incorporate compliance into every step of the healthcare software development life cycle from our dedicated guide.
5.
Deployment and support
Once the development and testing phases are complete, the system is deployed into the production environment. This involves careful planning for data migration (e.g., existing policies, employee records, historical training data) and integration with live systems. Initial deployment often focuses on a limited compliance domain (e.g., HIPAA Security routines) to validate system effectiveness before broader rollout.
Post-deployment, support teams continuously monitor system performance, security, and data integrity to address any remaining issues. Comprehensive software documentation, including configuration and maintenance guides, API specifications, and user manuals, is finalized to support future maintenance and upgrades.
Healthcare Compliance Management System Costs
The development costs of healthcare regulatory compliance software typically range from $80,000 to $600,000+, depending largely on the functional scope and required integrations.
$80,000–$150,000
An MVP or pilot build that supports:
- Centralized policy & document management.
- Basic training management and certificate generation.
- Incident reporting with standard submission forms and manual routing.
- Simple compliance dashboards (policy acknowledgment status, training completion).
- Notifications and reminders.
- Integration with HRIS.
$150,000–$300,000
A mid-tier build that covers all the MVP features, plus:
- Automated workflows for policy distribution, approvals, and training assignment.
- Risk assessment tools with corrective action plans.
- Vendor monitoring.
- Incident investigation workflows and automated incident analysis.
- Integration with EHR, ERP, vendor portals, and ticketing software.
- Enhanced compliance reporting and audit trail documentation.
$300,000–$600,000+
An enterprise-grade system covering the previous two tiers, plus:
- Smart workflow automation with AI-driven task routing and prioritization.
- Automated regulatory intelligence and continuous compliance monitoring.
- Intelligent modules for predictive risk analytics, anomaly detection, document analysis, etc.
- Multi-location and multi-entity management with customizable workflows.
- Integrations with all the necessary systems.
Why Build Compliance Management Software With ScienceSoft
- Since 2005 in medical software engineering.
- Since 2003 in cybersecurity.
- 150+ successful healthcare IT projects.
- In-house consultants with Medical Doctor degrees and up to 20 years of experience in the sector.
- Proficiency in healthcare-specific regulations (incl. HIPAA, HITECH, CMS Conditions of Participation, OSHA, and state-level mandates).
- Hands-on experience with health data exchange standards (HL7, FHIR, CDA, CCD, Blue Button+, and more)
- Implementing secure and transparent AI since 1989.
- 550+ developers, 50% of whom are seniors or leads with 9–20 years of experience.
Our awards and partnerships
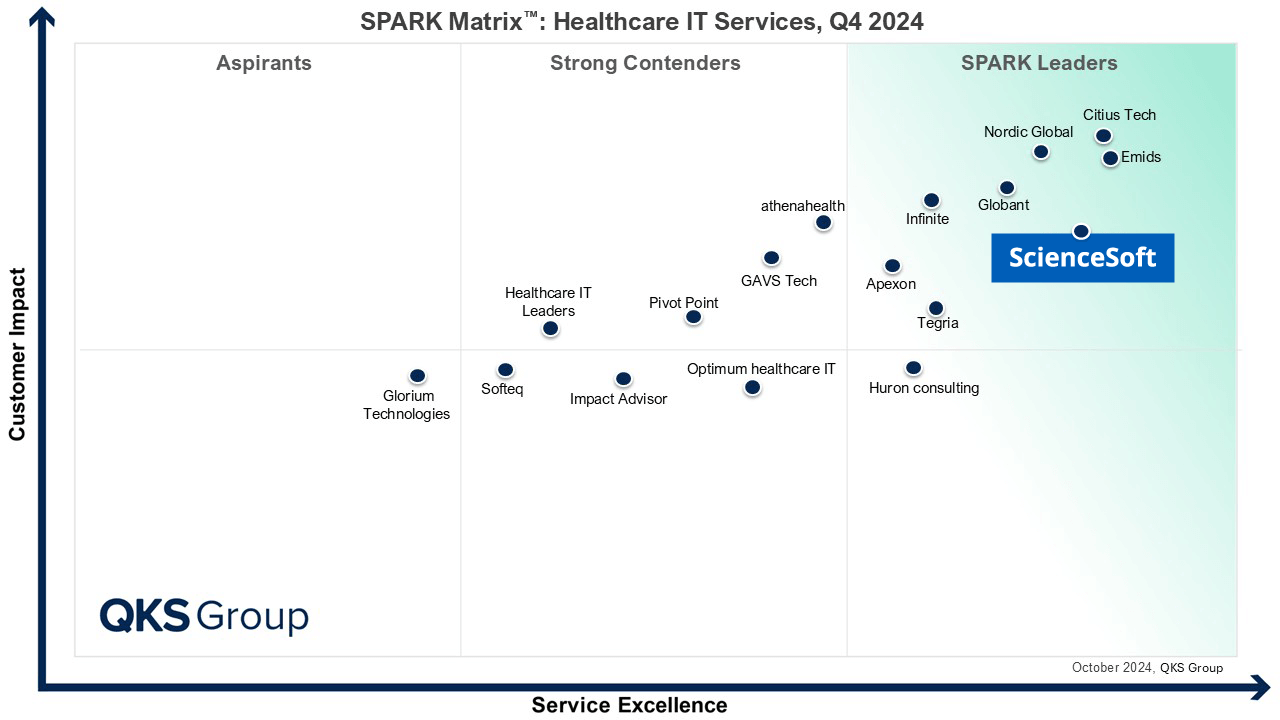
Featured among Healthcare IT Services Leaders in the 2022 and 2024 SPARK Matrix
Named among America’s Fastest-Growing Companies by Financial Times, 4 years in a row
Recognized on Newsweek’s 2025 America’s Most Reliable Companies List
Recognized by Health Tech Newspaper awards for the third time

Top Healthcare IT Developer and Advisor by Black Book™ survey 2023
Named Best in Class in Medical Device Connectivity by Frost & Sullivan (2023)
Listed in IAOP’s 2025 Global Outsourcing 100 for the 4th year running
ISO 13485-certified quality management system
ISO 27001-certified security management system





